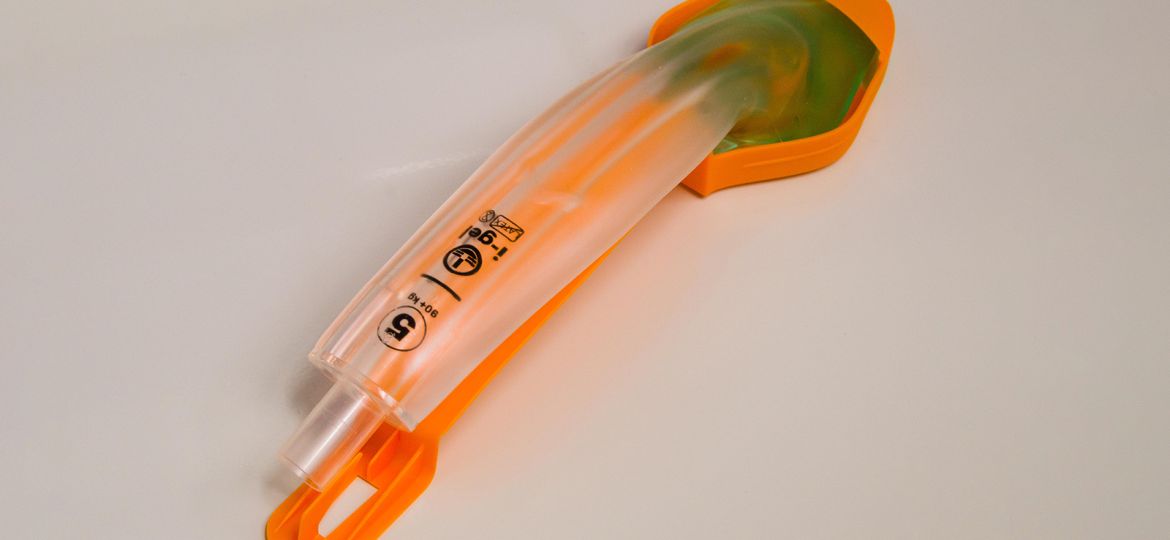
MedPage Today) — Supraglottic airway (SGA) devices used for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) were more successful at first attempt, but endotracheal intubation (ETI) has dominated as the initial strategy used by emergency medical services…
🛡️ Verifying that you are not a bot ⏳ Verifying your browser… ✓ Verification Complete This page will redirect in a moment…
🛡️ Verifying that you are not a bot ⏳ Verifying your browser… ✓ Verification Complete This page will redirect in a moment…
🛡️ Verifying that you are not a bot ⏳ Verifying your browser… ✓ Verification Complete This page will redirect in a moment…
A marathon pushes the human body close to its limits. Legs tire, lungs burn and the heart works hard for hours on end. For years, that strain has raised an uncomfortable question: does running 26 miles actually damage the heart…
The 1800s saw the transition of the food industry from one of self-sufficiency to central mass production to support the urbanization of the population. The degree of separation from producer and consumer led to rampant adulteration with additives such as lead, opium and other toxic substances being added…
The secret to a healthier and “younger” heart lies in the vagus nerve. A recent study coordinated by the Sant’Anna School of Advanced Studies in Pisa and published in Science Translational Medicine has shown that preserving bilateral cardiac vagal innervation is an anti-aging factor. In particular…
A spike in shootings during the covid pandemic propelled community violence intervention, a field that aims to stop gun deaths at the root. Baltimore used federal funds to launch a violence prevention office. But President Donald Trump has throttled such funds and instead is sending troops into cities…
🛡️ Verifying that you are not a bot ⏳ Verifying your browser… ✓ Verification Complete This page will redirect in a moment…
🛡️ Verifying that you are not a bot ⏳ Verifying your browser… ✓ Verification Complete This page will redirect in a moment…